Region Reconnoiters on 30×30 Aspirations
Keeping a third of California land unpaved might seem ambitious in a state where the car remains king, but even politicians are cozying up to the idea, at least in theory. Both Governor Newsom and President Biden have committed to the global 30×30 initiative, which aims to preserve 30% of the world’s land and water by 2030. “[The initiative] builds off of biologist E. O. Wilson’s call to conserve half of the Earth: 30% is an important milestone on the way to 50%,” Annie Burke, executive director of the Together Bay Area coalition, explains.
However, California’s proposed budget for 2023-2024 includes a 43%, $561 million cut to coastal resilience funding according to the Sierra Club, which could significantly hamper the state’s commitment to the 30×30 goals.
“It’s not 2030 yet, but we haven’t reached 30% yet either,” warns Burke. “Funding is really critical – we need to continue to make the case for climate resilience in the state budget and potential statewide law.”
To advocate for this funding, Together Bay Area – a regional coalition of over 70 nonprofits, public agencies, and Native American tribes – has collated around 117 projects that further the 30×30 milestones. From South Bay salt pond preservation to Sonoma lands restoration to new outdoor trails, these hyper-local projects aim to preserve the Bay’s unique micro-climates and mitigate the effects of climate change. The coalition hopes that their list provides a powerful model for what 30×30 entails in practice: a collective region-wide response to climate adaptation. “None of these projects are done in isolation,” Burke explains. “Public agencies work with nonprofits, and vice versa. They all end up being multi-benefit and multi-partnered.”
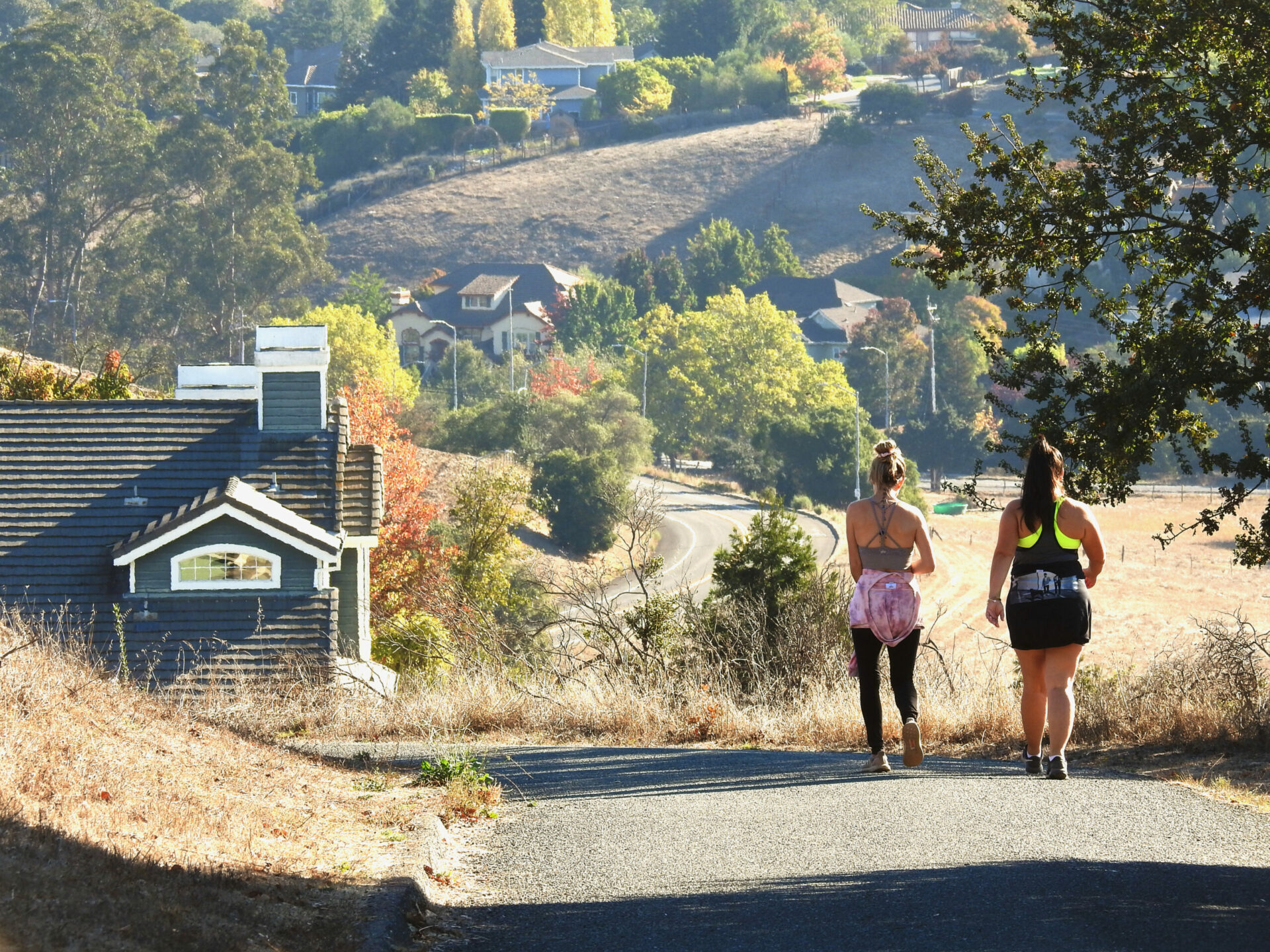
Parklands hosting rare blue oaks at the edge of Solano County sprawl. Photo: Robin Meadows.
Though implementing these projects would cost an estimated $700 million, it would also create 19,000 jobs, increase the economic value of California land, and foster resilience to climate change-related natural disasters. California wetlands, for example, function as sponges for sea level rise; coastal forests decrease wildfire risk; and both act as biodiversity hotspots for vital flora and fauna.
The Governor’s Office finalizes the California state budget in May, and the Bay Area coalition plans to keep fighting for climate resilience projects even in a period of relative austerity. Burke says, “I understand the need for a balanced budget, but we just don’t believe that this is where those cuts should happen. Without biodiversity, we as a species are in big trouble. Nature-based solutions pay off in the long run, because it doesn’t get cheaper to deal with these issues: they become more expensive.”
Burke isn’t daunted by the challenges. “A lot of people, a lot of money, and a lot of energy are going towards climate resilience. Depending on where you cast your eyes, you can see a lot of good.”
Other Recent Posts
CEQA Reforms: Boon or Brake for Adaptation?
California Environmental Quality Act updates may open up more housing, but some are sounding alarms about bypassed environmental regulations.
Repurposing Urban Lots & Waterfronts: Ashland Grove Park, Palo Alto Levee, and India Basin
In this edition of our professional column, we look at how groups are reimagining a lot in Ashland Grove and shorelines in San Francisco and Palo Alto.
Backyard Harvests Reduce Waste
A Cupertino Rotary Club program led by Vidula Aiyer harvests backyard fruit and reduces greenhouse gases.
Digging in the Dirt Got Me Into Student Climate Action
A public garden at El Cerrito High School in the East Bay inspired my love of nature and my decision to study environmental science at UCLA.
King Kong Levee: Two Miles Done, Two To Go
Two miles of levee are now in place as part of the project to protect Alviso and parts of San Jose, but construction will last much longer.
Making Shade a Priority in LA: An Interview with Sam Bloch
After witnessing fire disasters in neighboring counties, Marin formed a unique fire prevention authority and taxpayers funded it. Thirty projects and three years later, the county is clearer of undergrowth.
Without Transit Rescue Measure, Bay Area Faces Major Climate Setback
BART, Caltrain, Muni, and AC Transit could face devastating cuts, pushing thousands more cars onto Bay Area roads, unless voters intervene.
What I Learned About Sea Level Rise at a Regional Summit
Activists, planners and scientists say bay fill, equity and education are key concerns in the battle against future flooding.
How Two Rivers Could Rescue Sinking Beaches and Marshes
As new research hones in on the importance of sediment transfer, two rivers may hold the key to rescuing beaches and wetlands in Santa Cruz and the Bay Area.
One Man’s Five-Fire Learning Curve
Since Steve Rasmussen and his wife bought a Napa vineyard in 2015 they’ve weathered five fires, and learned how the county and the community respond when disaster strikes.