Global Study Finds Adaptation Progress Local Not Societal
Behind the public fanfare and declarations of international climate negotiations, like the COP26 conference that just ended in Glasgow, are thousands of researchers on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) who toil for years to summarize the science on every aspect imaginable of climate change so policymakers have the best available facts to work from. But when hundreds of scientists working on the IPCC tried to summarize the research on how humans are adapting to climate change, they ran into a big problem: nobody was keeping track.
“A lot of times they’re mapping adaptation intentions or policies, like what do governments want to do?” explains Kripa Jagannathan, a UC Berkeley scientist. “But what is actually happening … wasn’t actually mapped out.”
The resulting Global Adaptation Mapping Initiative, or GAMI, ultimately roped in more than 120 scientists from across the world, over three years, to screen nearly 50,000 scientific papers published about adaptation to climate change within the last decade. The unfunded, international effort, which Jagannathan describes as “an absolutely crazy project,” was led by Lea Berrang-Ford at the University of Leeds in the U.K. and culminated in a massive summary published in October 2021.
Analyzing the 1,682 research papers that described adaptations already underway showed that societies across the world are starting to change to better confront the climate crisis. But “responses to climate change were largely local and incremental, with limited evidence of rapid, extensive, or transformative change,” wrote the research team. And they found “negligible evidence of risk reduction, the underlying aim of adaptation.”
For example, research about building seawalls or people migrating away from a high-risk region is already skewed towards papers about the best way to do it in theory, or considerations of ethics and policies; the seawalls and people in these articles are imaginary. But even among research focusing on real-life people and places trying to be more resilient to climate change, very little addresses whether it’s working. Are the seawalls really protecting people better? Are people migrating from their homes any safer for doing so?
Avery Hill, a Stanford researcher who assisted with the scientific grunt work of organizing some of the papers, says that while the results were unsurprising, they can be powerful if used to shape future research and policy.
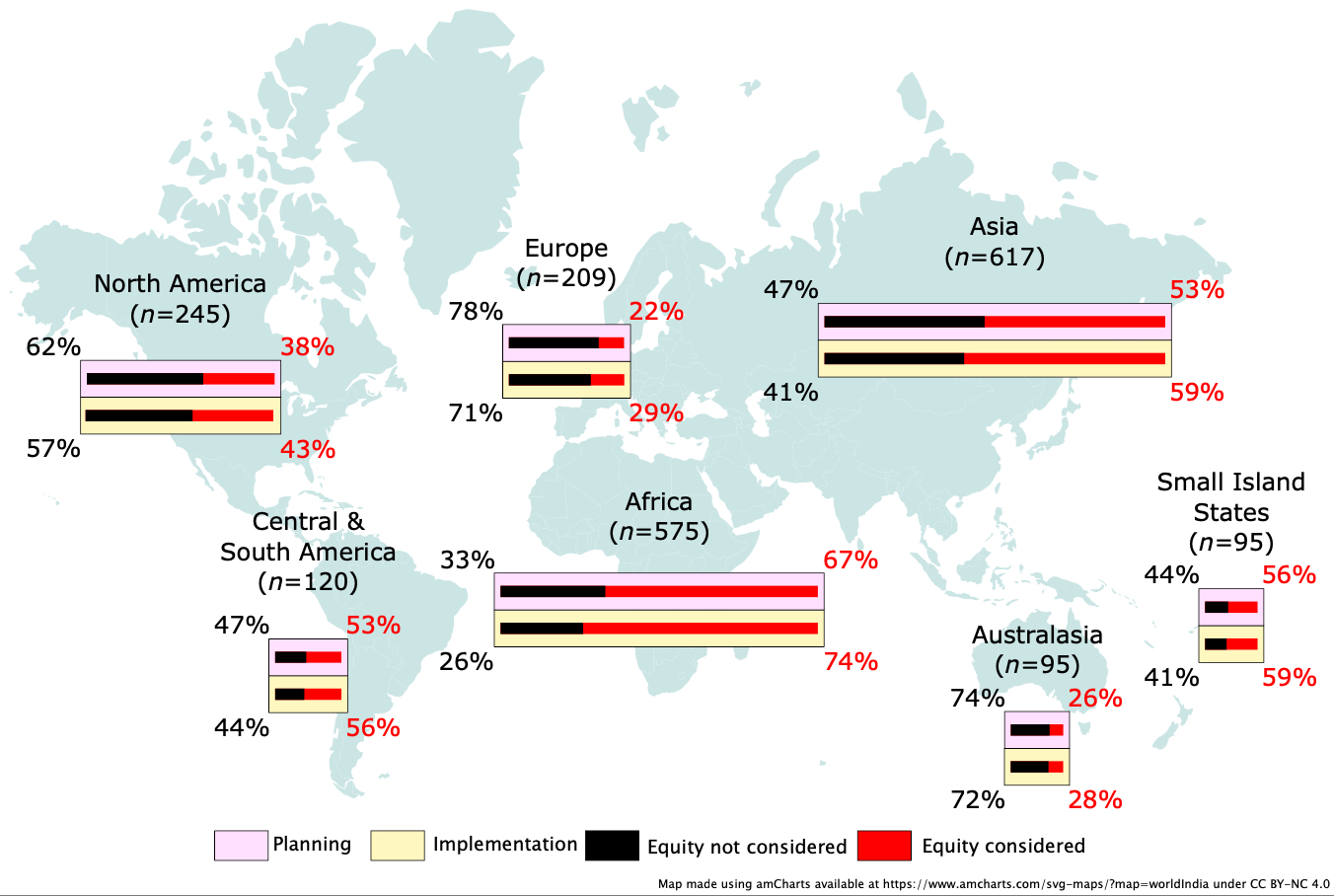
That’s already occurring to a degree. The mapping initiative inspired two dozen of the involved researchers, including Jagannathan, to launch another major analysis from the same database of scientific papers—this time, focused on equity in climate adaptation research. The team found that climate adaptation research in North America, Europe, and Australasia was unlikely to consider equity; the same went for adaptation articles about cities. The people most at risk of more extreme climate damages when equity is ignored include women, Indigenous groups, and low-income populations.
“People are responding to climate change because it’s affecting a lot of people, but it’s not enough,” says Hill. “And it’s not really happening at the right scale.”
Other Recent Posts
Gleaning in the Giving Season
The practice of collecting food left behind in fields after the harvest is good for the environment and gives more people access to produce.
New Study Teases Out Seawall Impacts
New models suggest that sea walls and levees provide protection against flooding and rising seas with little effect on surrounding areas.
Oakland High Schoolers Sample Local Kayaking
The Oakland Goes Outdoors program gives low-income students a chance to kayak, hike, and camp.
Growing Better Tomatoes with Less Water
UC Santa Cruz researchers find the highly-desired ‘Early Girl’ variety yields more tomatoes under dry-farmed conditions.
Santa Clara Helps Homeless Out of Harm’s Way
A year after adopting a controversial camping ban, Valley Water is trying to move unsheltered people out of the cold and rain.
The Race Against Runoff
San Francisco redesigns drains, parks, permeable pavements and buildings to keep stormwater out of the Bay and build flood resilience.
Learning the Art of Burning to Prevent Wildfire
In Santa Rosa’s Pepperwood Preserve, volunteers are learning how controlled fires can clear out natural wildfire fuel before it can spark.
Martinez Residents Want More Than Apologies — They Want Protection
After a 2022 release of toxic dust and a February 2025 fire, people in the northeast Bay town are tired of waiting for safety improvements.
Weaving Fire Protection Out Of What’s Already There
A new Greenbelt Alliance report shows how existing vineyards, grasslands, and managed forests can slow wildfire and save vulnerable homes.
Fall Plantings Build Pollinator Habitats in Concord
Community groups, climate advocates and a church are coming together to plant pollinator gardens as monarchs, bees see population declines.