Less Sea Level Rise for Left Coast
Scientists are now more confident we should plan for up to a foot of sea-level rise on the Pacific Coast by 2050 than they were the last time they did the math. That’s because this time when they compared the projections from computer models with projections from actual tide gauges in coastal waters and satellite altimetry (bouncing radar off the ocean surface to measure height changes), they got the same results.
“What’s new is that models and observation-based projections corroborate each other,” says US Geological Survey coastal hazard scientist Patrick Barnard. “We’re getting better at using multiple lines of evidence to support projections.”
The sea-level-rise science, released by an interagency federal task force (NOAA, USGS, FEMA, et al) this February, builds on scenarios in the recent Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s Sixth Assessment. For the US coastline in general, the report projects an average rise of 10-12 inches within the next 30 years. The East Coast could go higher (up to 14 inches), and the Gulf Coast higher still (up to 18 inches), while the West Coast could be lower (4-8 inches). Scientists were also confident enough about the new, ground-truthed math that they threw out a more extreme earlier projection.
“We’re pretty confident now about what we’ll see by 2050, but after that depends on emissions scenarios and the speed of ice sheet response,” says Barnard, a co-chair of the task force. “The latest science out of Antarctica is that despite observed ice sheet instability, and even if there is catastrophic loss, sea level will likely take longer to respond than what was originally thought possible.
While the near-future news is better for the West Coast than for other coasts, the San Francisco Bay Area will still suffer because so much of its infrastructure is built at low elevations right along the shoreline, often on sinking Bay fill. USGS projects 150,000 people and $50 billion worth of property across California are at risk of coastal flooding given the new 2050 projection. The Bay Area accounts for two-thirds of statewide impacts, says Barnard.
The East and Gulf coasts will be worse off mainly because they are sinking. “They have some of the highest rates of land subsidence in the country,” says Barnard, pointing out the Gulf Coast’s long history of oil and gas drilling and groundwater removal, and both coasts’ big muddy deltas and estuaries “that settle and sink over time.” Warmer water off these coasts also adds more volume to the ocean in these areas that cooler currents off the West Coast prevent.
Another difference in the three coasts is relief. The East and Gulf coasts are relatively flat, with few coastal mountains to stop the advance of storm surges and sea-level rise, and many wide-mouthed estuaries to invite these waters in. California’s coastal mountains, rocky shores, and narrow-mouthed estuaries (like the Golden Gate) reduce some impacts of sea-level rise.
Other sorts of flooding aren’t so stymied by California’s steep shores. The November 2021 atmospheric river over the Pacific sent torrents down hillsides to pool at the base of Marin County watersheds, for example, just where the Bay is also creeping inland, pushing groundwater higher, too.
Other Recent Posts
Boxes of Mud Could Tell a Hopeful Sediment Story
Scientists are testing whether dredged sediment placed in nearby shallows can help our wetlands keep pace with rising seas. Tiny tracers may reveal the answer.
“I Invite Everyone To Be a Scientist”
Plant tissue culture can help endangered species adapt to climate change. Amateur plant biologist Jasmine Neal’s community lab could make this tech more accessible.
How To Explain Extreme Weather Without the Fear Factor
Fear-based messaging about extreme weather can backfire. Here are some simple metaphors to explain climate change.
Live Near a Tiny Library? Join Our Citizen Marketing Campaign
KneeDeep asks readers to place paper zines in tiny street libraries to help us reach new folks.
Join KneeDeep Times for Lightning Talks with 8 Local Reporters at SF Climate Week
Lightning Talks with 8 Reporters for SF Climate Week
ReaderBoard
Once a month we share reader announcements: jobs, events, reports, and more.
Staying Wise About Fire – 5 Years Post-CZU
As insurance companies pull out and wildfire seasons intensify, Santa Cruz County residents navigate the complexities of staying fire-ready.
Artist Christa Grenawalt Paints with Rain
Snippet of insight from the artist about her work.
High-Concept Plans for a High-Risk Shoreline
OneShoreline’s effort to shield the Millbrae-Burlingame shoreline from flooding has to balance cost, habitat, and airport safety.
In a Climate Disaster, Your Car Won’t Save You
Fleeing wildfires without a car might seem scary, but so is being trapped in evacuation gridlock — and the hellscape of car-dependency.
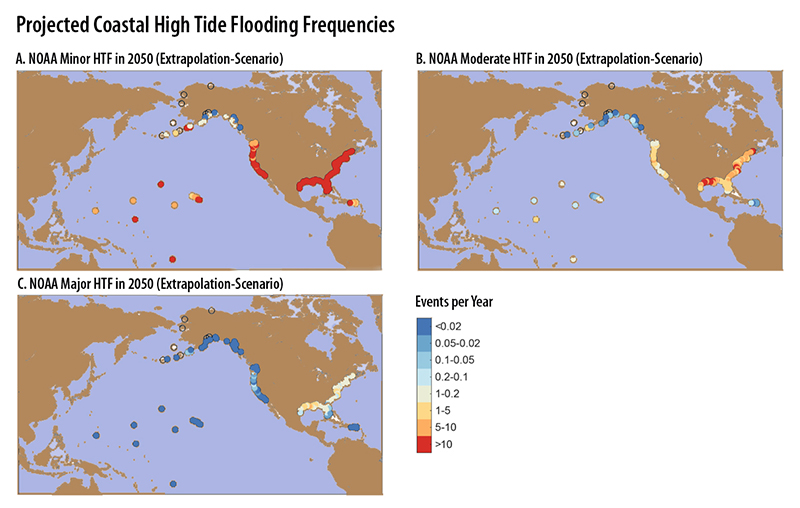
Projected coastal flooding frequencies in the US by 2050. Source: NOAA/USGS.
“Flood frequency is also going to increase exponentially with sea-level rise,” says Barnard. According to the new science, by 2050 damaging flooding will occur more than ten times more often than it does today, or about four times a year as compared to once every three years at present. Though the science also projects flooding will be a bit less frequent in California than on the other coasts, it’s still a worry. “Everything is going to be riding on top of an extra foot of sea level, which could tip the scales in many low-lying coastal communities.”
Everything is also riding on when and how those ice sheets melt, and where in our oceans the melt water ends up. Barnard says just because one coast may be closer to melt sources than another does not mean it will experience higher sea levels — but sorting that all out requires much more complex science.
We can now plan with more certainty for one foot of sea-level rise by 2050. But beyond that is the stuff of politics and the profit motive. Even the best science can’t account for the uncertainties of human meltdown.